Australia Education System
The education system in Australia provides top-notch opportunities for international students seeking a world-class academic and individual experience. Australian education is highly regarded and widely recognized worldwide. The system offers diverse courses, covering 12 years of primary and secondary education, along with a vast range of study programs, including traditional academic programs and practical vocational courses.
Primary School
Primary education in Australia consists of seven years of preliminary schooling. Children commence their education at the age of five (Year 1) and complete it by the age of 12 (Year 7). This level provides foundational education, preparing students for society and the next level of education.
Secondary School
Students transition to secondary school at the age of 12 (Year 8). It is mandatory to complete two years of ‘junior high school’ (up to Year 10). After Year 10, students can either discontinue formal education or pursue further studies. Those continuing must complete an additional two years of high school (Year 11 and Year 12) to earn their high school diploma. Students who leave after Year 10 may opt for vocational education courses or apprenticeship training to enter the workforce.
Tertiary Education
After completing Year 12, students can pursue higher (tertiary) education, including Bachelor’s, Master’s, and Doctoral degrees. Tertiary education in Australia operates under the Australian Qualifications Framework (AQF), integrating both vocational and higher education into a unified classification.
Types of Higher Education Courses
Vocational Education & Training (VET)
VET courses are offered by TAFE (Technical and Further Education) colleges and private institutions. These courses typically last 1-2 years, providing industry-relevant skills and employment opportunities.
Diploma (1-2 years): A higher professional qualification offering specialized training.
Advanced Diploma (2 years): A higher-level qualification that may provide advanced standing into a Bachelor’s program.
Associate Degree (2 years): Focuses on academic and workplace skills, providing credit transfer options into a Bachelor’s program.
Bachelor’s Degree
A Bachelor’s degree is a highly regarded qualification worldwide. Australian universities offer:
3-year general degrees
4-year professional degrees
Honours degrees (1 additional year of research-based study)
Combined degrees (dual specialization options)
Foundation courses (for students who need additional academic preparation)
Postgraduate Education
Admission to a Master’s degree program requires a Bachelor’s degree or relevant work experience. Programs include:
Master’s Degree by Coursework
Master’s Degree by Research
Professional Master’s Degree
Doctoral Degrees
Doctoral degrees are the highest level of academic qualification in Australia.
Research Doctorate (PhD): Requires a research-based Master’s degree or Honours Bachelor’s degree.
Professional Doctorate: Combines research and coursework, requiring an Honours or Master’s degree.
Credit Transfer
Credit transfer allows students to receive recognition for prior study, reducing redundancy and providing flexible pathways between courses and institutions.
Academic Year
The academic year in Australia runs from February to November, with many institutions also offering a July intake. Some universities operate on a trimester or term-based calendar.
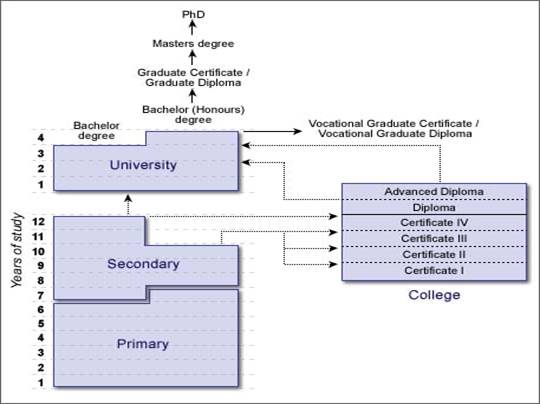
Study Pathways in Australia
Year 10 → Year 11 → Year 12 → University / Vocational Program (Certificate 1-3 / Apprenticeship)
Vocational Pathway:
Certificate IV → Diploma → Advanced Diploma → Bachelor’s Degree (Year 2 or 3, based on credit transfer)
Higher Education Pathway:
Bachelor’s Degree → Honours (Optional) → Master’s Degree → PhD
The Australian education system is globally recognized, offering excellent career opportunities and pathways to permanent residency for qualified students.
The diagram should visually represent the different pathways students can take through the Australian education system. Below is a suggested hierarchical flow:
1. Primary & Secondary Education Pathway
- Year 1 – Year 7 (Primary School)
↓ - Year 8 – Year 10 (Junior High School)
- Option 1: Continue to Year 11 & Year 12 (Senior High School)
- Option 2: Exit school & enroll in Vocational Education (Certificate I-III) or Apprenticeship
2. Post-Year 10 Study Pathways
-
If completing Year 12:
- Option 1: Direct entry into a Bachelor’s Degree
- Option 2: Enroll in a Foundation Program (for international students) before a Bachelor’s
- Option 3: Pursue a Certificate IV, Diploma, or Advanced Diploma under VET
-
If leaving after Year 10:
- Option 1: Start a Certificate I-IV or Apprenticeship
- Option 2: Enroll in a Foundation Course
- Option 3: Gain work experience and later pursue further education
3. Vocational & Higher Education Pathways
-
Vocational Pathway:
- Certificate IV → Diploma → Advanced Diploma
- Option to transfer into Bachelor’s Degree (Year 2 or 3, depending on credit transfer)
-
Higher Education Pathway:
- Bachelor’s Degree (3-4 years)
- Honours Degree (Optional, 1 year)
- Master’s Degree (Coursework/Research, 1-2 years)
- Doctoral Degree (PhD, Research, 3+ years)
References:
Admission Support Kit – Australia
| Admission Checklist | GS Guidelines | Visa Checklist | |||



