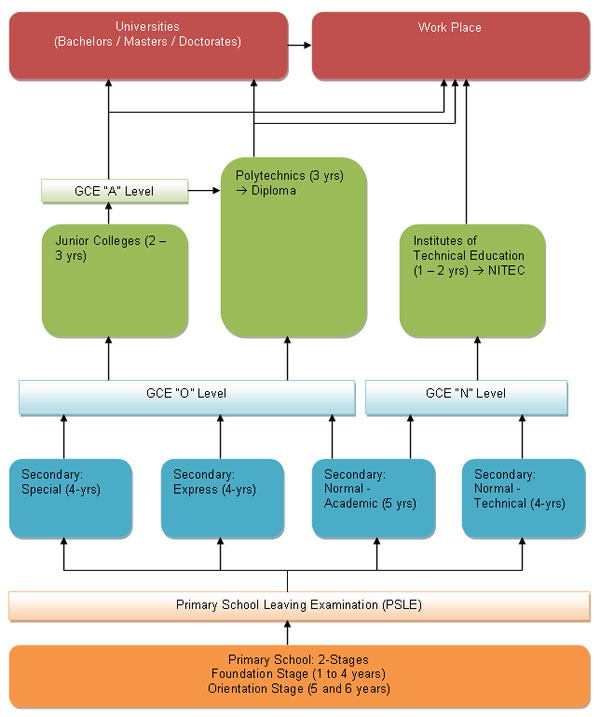
Education in Singapore follows the four-tier model which includes primary schools, followed by secondary schools, pre-tertiary level at Junior Colleges or Polytechnics and tertiary education at a university.
Primary Education
Primary Education in Singapore is free and compulsory Primary education starts at age seven and consists of 2 stages – a four year foundation stage (Primary 1 to 4), a two year orientation stage (Primary 5 to 6). At the end of Primary 6, students have to take the national Primary School Leaving Examination (PSLE) and are placed in the secondary schools according to performance in the PSLE.
Secondary Education
Based on results of the PSLE, students are placed in different secondary education tracks or streams: “Special”, “Express”, “Normal (Academic)”, or “Normal (Technical)”.
“Special” and “Express” are four-year courses leading up to the Singapore-Cambridge GCE O’ Level examination.
Normal is a four-year course leading up to a Normal-level (N-level) exam, with the possibility of a fifth year followed by an O-level.
Pre-Tertiary
Upon completion of the 4- or 5-year secondary school education, students (excluding IP students) will participate in the annual Singaporean GCE ‘O’ Level, the results of which determine which pre-universities or post-secondary institutions they may apply for.
Pre-university centres include junior colleges for a two-year course or Millennia Institute for a three-year course, both leading up to GCE ‘A’ Level. These institutions emphasize on academics than professional technical education. Students who wish to pursue for a professional-centred diploma education go on to post-secondary institutions such as the polytechnics and the Institute of Technical Education (ITE).
Tertiary
After completion of two-year or three-year courses in Junior Colleges or Millennia Institute, students may go ahead to earn degrees awarded in the Universities.
Polytechnics
Polytechnics in Singapore provide 3-year diploma courses and, they accept students based on their GCE “O” level, GCE “A” level or Institute of Technical Education (ITE) results.
Polytechnics offer a wide range of courses in various fields, including engineering, business studies, accountancy, tourism and hospitality management, mass communications, digital media and biotechnology. There are also specialized courses such as marine engineering, nautical studies, nursing, and optometry. They provide a more industry-oriented education as an alternative to junior colleges for post-secondary studies.
Graduates of polytechnics with good grades can continue to pursue further tertiary education at the universities, and many overseas universities, notably those in Australia, New Zealand and the United Kingdom.
Institute of Technical Education
The Institute of Technical Education (ITE) accepts students based on their GCE “O” level results and they provide 2-year courses leading to a locally recognised National ITE Certificate (NITEC).
Universities
Universities provide both undergraduate education and postgraduate education and grant academic degrees in a variety of subjects.
Universities accept students after GCE “A” Level or diplomas from Polytechnics.
Singapore Education Landscape
Admission Support Kit – Singapore
| Admission Checklist | SOP- Guidelines |
SOP – Do’s & Dont’s |
|||
| Sample SOP | Resume – Guidelines | Resume – Sample | |||
| CV v/s Resume | General RECO Letter |
Business RECO Letter |
|||
| CV – Guidelines | CV – Sample |



