New Zealand Education System
Education in New Zealand follows a three-tier model, comprising primary schools, secondary schools (high schools), and tertiary education at universities, polytechnics, or private institutions.
Education is free and compulsory for children between the ages of 6 and 16. However, most children start school at the age of 5. Post-compulsory education is regulated within the New Zealand Qualifications Framework (NZQF), which ensures a unified system of national qualifications across schools, vocational education, and higher education institutions.
The academic year in New Zealand varies between institutions but generally follows this structure:
- Primary and Secondary Schools & Polytechnics: Late January to mid-December
- Universities: Late February to mid-November
School Education
Most schools in New Zealand cater to primary, intermediate, and secondary school students, categorized as follows:
- Years 1–6: Primary School (Ages 5–10)
- Years 7–8: Intermediate School (Ages 11–12)
- Years 9–13: Secondary School (Ages 13–18)
Students in secondary school work towards the National Certificate of Educational Achievement (NCEA), which is the main qualification for high school students.
Tertiary Education
Tertiary education in New Zealand includes universities, polytechnics & institutes of technology, and private training establishments.
Universities
New Zealand has eight government-funded universities, offering undergraduate and postgraduate degree programs in academic and professional fields. These universities offer a wide range of programs, including Commerce, Science, Arts, Engineering, Computer Science, Medicine, and Agriculture.
New Zealand universities are internationally recognized, and many graduates have achieved global success in their fields.
Polytechnics and Institutes of Technology
New Zealand has 16 Institutes of Technology and Polytechnics (ITPs) that offer both academic and vocational programs. These institutions provide a practical, hands-on learning experience, and some offer degree-level programs in specialized fields.
Private Tertiary and Training Establishments (PTEs)
New Zealand also has numerous Private Training Establishments (PTEs), offering alternative study options. These institutions provide certificates, diplomas, and degrees in various subjects such as hospitality, IT, arts, tourism, business, and management.
New Zealand Qualifications Framework (NZQF)
The New Zealand Qualifications Framework (NZQF) is a nationally recognized system that ensures high-quality education standards across institutions.
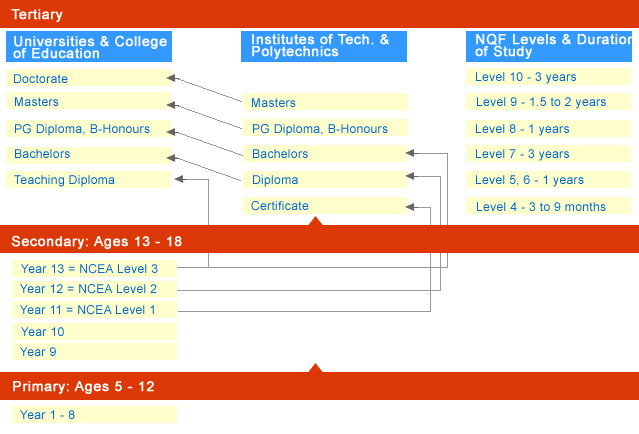
Qualification Levels in New Zealand
All qualifications within the NZQF are divided into 10 levels, based on the complexity of skills and knowledge imparted:
| Level | Qualification |
|---|---|
| Level 1-3 | Certificates (Foundation and Entry-Level Courses) |
| Level 4-6 | Diplomas (Vocational and Technical Training) |
| Level 7 | Bachelor’s Degree & Graduate Diplomas |
| Level 8 | Postgraduate Certificate/Diploma |
| Level 9 | Master’s Degree |
| Level 10 | Doctoral (PhD) Degree |
The NZQF ensures that all qualifications are internationally recognized, making New Zealand an excellent destination for students seeking global career opportunities.
All qualifications within the NZQF are categorized into levels according to the complexity of skills and knowledge they encompass. These levels do not correspond to the duration of study but rather to the depth and scope of the qualification’s content. The following qualifications are available within the NZQF:
NQF Qualifications and Levels:
Admission Support Kit – New Zealand
| Admission Checklist | SOP- Guidelines |
SOP – Do’s & Dont’s |
|||
| Sample SOP | Resume – Guidelines | Resume – Sample | |||
| General RECO Letter |
Business RECO Letter |
||||



